Import Template Calculation
This section describes the properties of the Excel template (Version: 9.0.0.1) for importing and updating the Should CostingSolution.
Each release provides you with new Excel templates for the import into the FACTON Should Costing Solution.
Download the Excel Templates:
| Excel template: Calculation | |
| Excel template: Sub-structure of a calculation |
You can import a calculation with referenced master data into FACTON.
| Excel template: Material (incl. Value Rules) | |
| Excel template: Calculation with referenced master data | |
Structure of Excel Templates
Metadata of Excel Templates
The metadata of the Excel template is required for the correct allocation of the imported data and should not be edited. In the orange table, you maintain the metadata or data that applies equally to the entire data table.

- SheetVersion shows the version of the Excel template.
Data Table
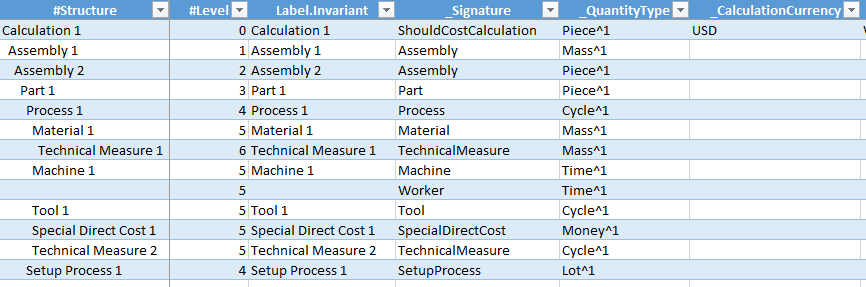
Figure: Extract of the Excel template
Excel Rows
With every Excel row, you determine an additional calculation element for the import.
For each of these calculation elements you have to indicate the level depending on the element above or below - with the help of a numeration in the #Level column.
For an import of a complete calculation, the top-level element is equal to the calculation and thus must have the lowest number, e.g. "0".
For an import of a sub-structure, several elements can have the lowest number.
Excel Columns
With every Excel column, you determine an additional property of the calculation element. The column names can vary with every release. The version of the Excel template has to match the release version of FACTON.
More columns for the Excel templates from FACTON can be added within the scope of customizing FACTON® or an authorized partner.
Required Columns
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| #Structure | Display of the calculation structure. This column is irrelevant for the import process; it only purposes visualizing the structure. |
| #Level | Display and input of the structural level of the element. This column is relevant for the import process only; it does not purpose building the calculation structure. |
| _Signature | Indication of the type of calculation element, e.g. assembly or material. |
Supported Data Types
Unit-Dependent Values
Master data with unit values (e.g. duration) always consist of two columns: one for the value and one for the unit.
The unit value duration of work steps consists of the properties:
| Duration.Number: | Value of the duration, e.g. 1 |
| Duration.Unit: | Unit of the duration, e.g. TMU |
Localized Values
Localized values can be shown as dependent or independent from language.
In order to show language-independent texts, you need to use "Invariant" as suffix (e. g. column "Label.Invariant" or "Description.Invariant"). In order to show language-dependent texts, use the ISO Two Letter Language Code as suffix for the property name (e.g. column "Label.de" and "Label.en").
you can fill in "Description", "Description (de)" and "Description (en)".
| Label.Invariant: | Text independent from language, e. g. Machine |
| Label.de: | Text dependent from language, e. g. (de) Spritzguss |
| Label.en: | Text dependent from language, e. g. (en) Injection Molding |
Boolean (Logical Values):
The boolean type has two value forms. The truth value is either "TRUE" or "FALSE" .
Integer
The number type is for integers.
Number
The number type is for floating point figures with or without decimal places. In FACTON, the values are rounded to the twelfth decimal place.
String
The text type is for character strings of variable length.
Date
The date type is for date specification.
Single-Selection List:
A single semantic key is entered into the single selection list.
Example
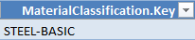
This entry of the Excel template in the FACTON client stands for the Material Classification "Basic Material > Metal > Steel > Basic Steel".
Multi-Selection List
Several semantic keys are entered into the multi-selection list.
The semicolon can be masked with the escape character "\".
Example

This entry of the Excel template in the FACTON client stands for the Manufacturing Methods "Primary Shaping > Casting" and "Primary Shaping > Extrusion".
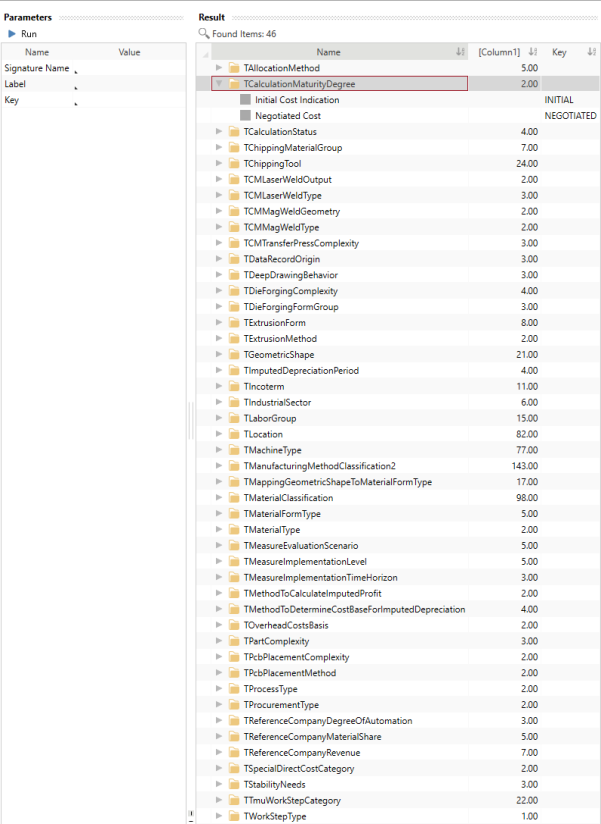
Identify Semantic Keys in FACTON
You can identify the semantic keys to use them for Excel imports by running queries in FACTON. The place where to use the semantic key in the Excel template is shown in the column XXX.Key.
Identify Semantic Keys
- You are logged in as SC Master Data Administrator.
- You are in the Master Data workspace.
- In the Explorer > Queries, click on ► in front of SC Solution Data.
- Click on Semantic Keys for Selection Lists.
A new tab "Query: Semantic Keys for Selection Lists" opens where you can determine specific query parameters.
- Define your query parameters.
- Click the
Run button to run the query.
All matching data are shown in the Result view.