Calculate Emissions
From version 14.1, you can include the emissions of machines and materials in your calculation. Emissions are aggregated along the bill of material structure in the calculation and are displayed alongside costs.
The various scopes of emissions (1-3) used to calculate machine or material emissions are based on the GHG Protocol ("Greenhouse Gas Protocol"), an internationally recognized standard for identifying and reporting greenhouse gas emissions. It was developed by the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD). The aim of the protocol is to provide companies, organizations and governments with a clear and consistent methodology for quantifying their greenhouse gas emissions. This is intended to help to effectively manage and reduce emissions and ultimately support global efforts to combat climate change.
The protocol includes various standards covering different emission sources and scopes, including direct emissions (scope 1), indirect emissions from purchased energy consumption (scope 2) and all other indirect emissions (scope 3) arising from an organization's value chain:
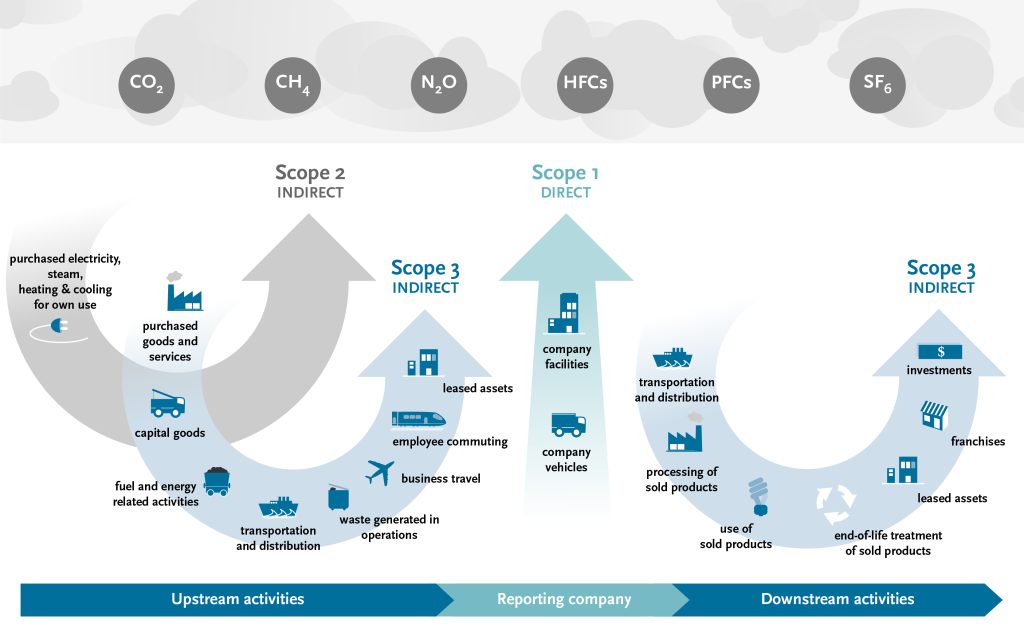
Figure: Emission scopes based on GHG Protocol (Source: https://ghgprotocol.org/blog/you-too-can-master-value-chain-emissions)
FACTON distinguishes between production-related emissions (scope 1 and 2), which are caused by the machine's consumption of gas (direct emissions) and electricity (indirect emissions), and upstream indirect emissions (scope 3), which arise during the life cycle of procured materials.
Scope 1 and 2 - Production-Related Emissions at Machines
Production-related emissions are mainly caused by the use of machinery.
In FACTON the total emission factor of the machine takes both direct (scope 1) and indirect (scope 2) emissions into account and is calculated on the basis of emission factors for electricity consumption and gas. The emission factor for electricity depends on the location and validity period and can be administered together with the emission factor for gas in the master data.
Emissions are calculated as soon as the machine is added to the calculation with maintained machine consumption values (gas, electricity).
Emissions can be calculated for all machines, i.e. all origins ("Own Company" or "FACTON").

Scope 3 - Upstream Emissions at Materials
Indirect, upstream emissions primarily occur for materials and are calculated in FACTON using the scope emission factor (EF) maintained directly at the material via local value rules.
As soon as the material is used in the calculation, the emissions are calculated automatically on the basis of the scope emission factor and the relevant quantity (for materials with quantity calculation, it also depends on the geometric shape).
Emissions can be calculated for all materials, i.e. of all quantity types (mass, area, length, piece, volume) and quantity calculations (coil, solid profile, etc.), as well as all origins ("Own Company" or "FACTON").
