Global Properties
Global properties are master data records that are not linked to a certain element. This is why they are described as being object-independent. Global properties give you additional information on the calculation and consist of cost rates, such as wages or the interest rate for the location. This information is independent of the Calculation Structure and the elements in the calculation. Global properties are not directly visible and cannot be inserted into the calculation like master data. You assign global properties to the calculation by selecting a location, for example, or adding an element to the calculation that the global properties are linked to.
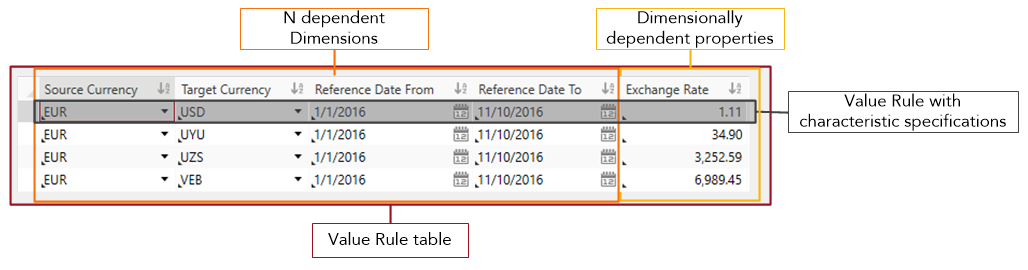
Global properties are dimensionally-dependent properties and are entered in the value rules tables.
Dimensions »Reference Date From« and »Reference Date To«
Only all-day values are available for the two dimensions.
Example:
| »Reference Date From« | »Reference Date To« | Interval Notation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value Rule | a | b | a ≤ x ≤ b or [a;b] |
| Value Rule 1 | 1/1/2018 | 12/31/2018 | [1/1/2018; 12/31/2018] |
| Value Rule 2 | 1/1/2019 | 12/31/2019 | [1/1/2019 00:00 UTC, 12/31/2019 24:00 UTC) |
| If the reference date of a calculation is 2018, value rule 1 applies, regardless of the time. | |||
Clicking a property opens a new tab with a value rule table for the selected property. The value rule table shows the global property and all properties on which it depends in the column header. The data records (rows) display the concrete values of the global property and their dependent values.
Under Global Properties in the Master Data workspace, you can define and maintain company-own exchange rates, location factors, overhead rates and wages.